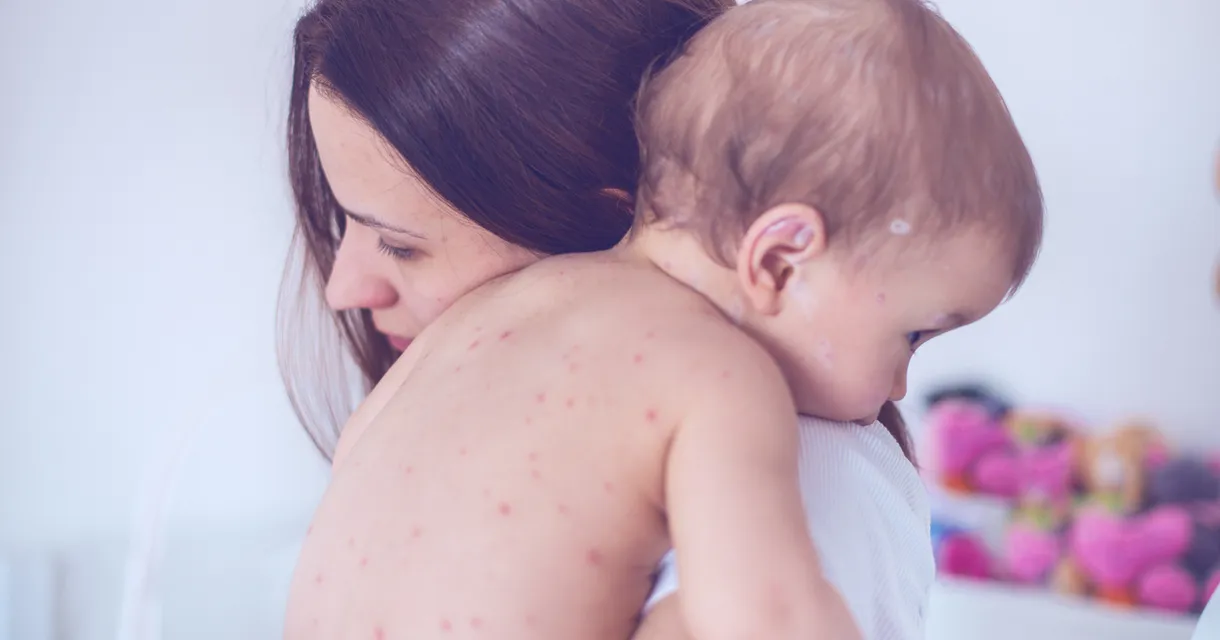
Chicken pox is a prevalent infectious disease that most individuals will contract at some point in their lives. Although it predominantly affects children, it is possible to contract it at any age. If you have not previously had chicken pox and someone in your household becomes infected, there is a high likelihood that you will also catch it due to its contagious nature.
For the majority of people, chicken pox does not pose a significant health threat. However, the infection can become more severe if you are elderly, have a compromised immune system, or are pregnant, as these conditions can increase susceptibility to complications. Continue reading to discover more comprehensive information about the virus, including the symptoms it presents, the underlying cause, and the number of times you might be susceptible to contracting chicken pox.
What Causes Chicken Pox?
Chicken pox is an infectious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. Approximately 90% of individuals who have not previously contracted chicken pox will become infected upon exposure to the virus. It is possible to contract chicken pox at any time of the year, though it is particularly prevalent during the spring months. The infection is most commonly observed in children under the age of 10, although it can affect individuals of any age who have not been vaccinated or previously exposed to the virus.
How Can You Catch Chicken Pox?
Chicken pox is highly contagious and can be contracted by being close to an individual who is carrying the virus. It is transmitted effortlessly through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, allowing the virus particles to spread. Additionally, you can become infected by coming into contact with surfaces or objects that have been touched by the person with the virus, or by direct contact with the fluid from the blisters of an infected person.
When is Chicken Pox Contagious?
Chicken pox can be transmitted to others starting from two days prior to the appearance of the characteristic spots and continues to be contagious until all the spots have crusted over and formed scabs, which usually occurs about five days after the spots first appear. In individuals who have been vaccinated against chicken pox, the disease may manifest as lesions that do not form scabs. These vaccinated individuals remain contagious until a full 24 hours have passed without the emergence of any new lesions.
How to Treat Chicken Pox at Home
If you catch chicken pox, you’ll need to stay home from school, work or nursery until the spots have formed a scab. Chicken pox can usually be treated at home, and helpful chicken pox remedies include:
-
Drinking plenty of fluids
-
Using cooling gels or creams from a pharmacy
-
Dressing in loose clothes
-
Bathing in cool water
-
Cut your child’s fingernails to prevent them from scratching
-
Taking paracetamol to help with pain and discomfort
Chicken pox should clear up by itself after one or two weeks. You should speak to a GP if you’re concerned about your child, or if you’re not sure whether it’s chicken pox.
Browse our relevant products:
-
Eurax Cream 10% 100g £7.10 save £2.39
-
Care Calamine Lotion 200ml £2.19 save £1.80
-
Care Virasoothe Chicken Pox Relief Cooling Gel 50g £5.65 save £1.84
Can You Catch Chicken Pox More Than Once?
It is possible to get chicken pox more than once, but it’s unusual. When you get chicken pox, the virus stays in your body, remaining dormant. However, it can be triggered again if your immune system is weak. This causes an illness called shingles.
Shingles results in a painful rash of blisters that cover one side of the face or body, and typically last about three weeks. It’s not possible to catch shingles from someone with chicken pox, but you can catch chicken pox from someone who has shingles if you have not had chicken pox before.
How Does the Chicken Pox Vaccine Work?
The vaccine works by protecting people from varicella zoster, the infectious disease that causes chicken pox. There are currently two vaccines available, which are the VARIVAX and VARILRIX chicken pox jab.
The vaccine contains weakened versions of the virus that causes the disease. Through vaccination, your immune system learns how to fight the virus much more quickly than it would if you were to catch and then treat it.
It is estimated that over 90% of children who receive both chicken pox vaccine doses acquire a lifetime immunity to chicken pox.
Book your Chicken Pox Vaccine Today
We’ve discussed how you can catch chicken pox, as well as the stages and symptoms of chicken pox, and home remedies you can use. Children and adults who are in regular or close contact with someone who has chicken pox should be vaccinated against it.
Find your nearest pharmacy offering the vaccine, and book your appointment today. After agreeing on a date, you will have your first dose. Our pharmacist will then book you in for the second dose a minimum of six weeks later - and then you’re done, it’s as easy as that.
Alongside the chicken pox vaccine, we also offer the seasonal flu vaccine.